Side-by-Side Comparison
Let’s compare some of the first images taken by the Webb telescope and compare it to images of the same location taken by Hubble.


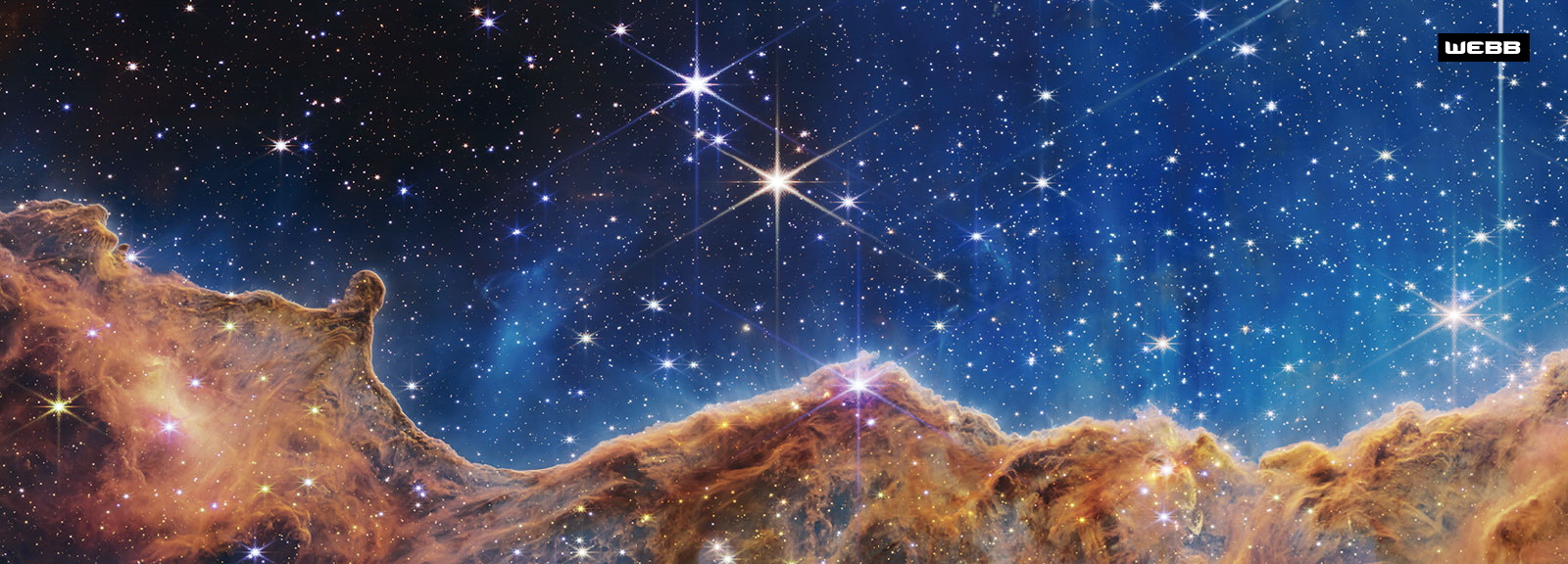
The telescopes took the images above of a region known as SMACS 0723, a cluster of galaxies about 4 billion light years from Earth within the southern constellation of Volans.
Note the elongated galaxies and stars. Their light has been stretched and deformed by an effect called gravitational lensing.






NASA and the other space agencies will release more images soon along with spectrographic analysis of exoplanet atmospheric composition.
In the end, it’s not just about the pretty pictures. It’s about the science.
Scott Manley
The Hubble and Webb Space Telescopes

Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble): Launched by NASA in 1990 by NASA/STScI.
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or Webb): Launched in December 2021 by a consortium of international organizations that include:
- STScI – The Space Telescope Science Institute, a division of NASA – the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration,
- ESA – the European Space Agency
- CSA – the Canadian Space Agency
In the months since its launch, the Webb Telescope has been cooling down, and the space agencies have put through a series of mirror adjustments and calibration routines. Since it has more sensitive infra-red detectors than the Hubble telescope, the agencies placed it in a higher orbit than Hubble. The orbit puts the Webb farther away from infra-red radiation from the Earth and Moon, but outside the zone that astronauts can service it.

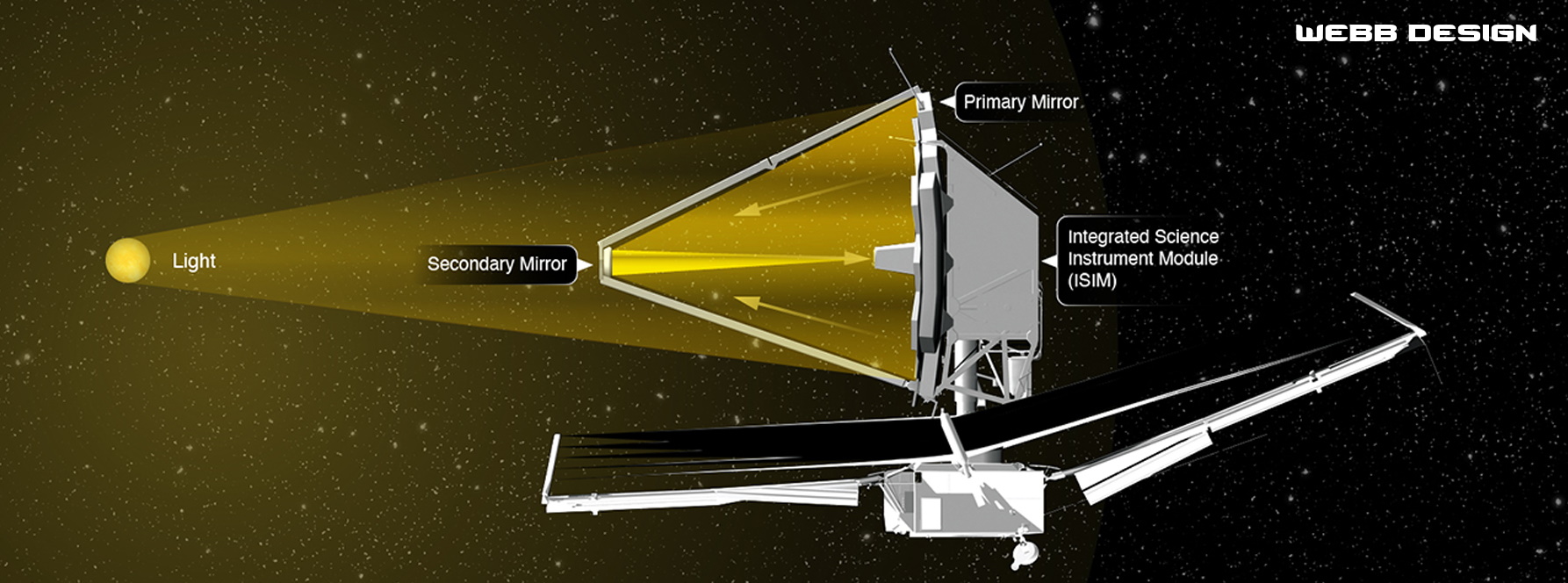
One of the key differences between the telescopes is the mirror size. The older Hubble telescope has a 2.4-meter mirror, whereas the Webb telescope is over two and a half times bigger at 6.5 meters. In the video below, note that the configuration of the mirrors is also different. Instead of one reflective surface, the Webb telescope uses eighteen hexagonal shaped mirrors. This gives it a larger reflecting surface but creates image artifacts as shown later.
Another major difference between the two space telescopes is how they gather light. The Webb telescope can peer farther into the infra-red end of the spectrum. This allows the images to show older objects in space, since light from older objects red-shifts over time.





Great insight. Well done.